Introduction
In agriculture, the use of biostimulants such as rhizosphere plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPR) and humic acid (HA) has been shown to improve many agronomic properties of plants while enhancing plant growth, yield, and resilience. These natural substances contain a variety of compounds that positively influence plant physiological processes. Biostimulants play a vital role in sustainable agricultural practices, from promoting root development to improving nutrient uptake efficiency.
Table of Contents
What are Biostimulants in Agriculture?
Biostimulants in agriculture are organic substances extracted from natural sources such as seaweed, humic acid, amino acids, and beneficial microorganisms. Unlike fertilizers, which provide plants with essential nutrients, biostimulants improve overall health and performance by promoting root development, improving nutrient uptake, and increasing stress resistance.
Research shows that biostimulants work at a molecular level to trigger plant physiological responses. By activating gene expression, regulating hormone levels, and stimulating metabolic pathways. Herbivores can also be directly affected by changes in secondary metabolites or anti-nutritional proteins (e.g. protease inhibitors, lectins).
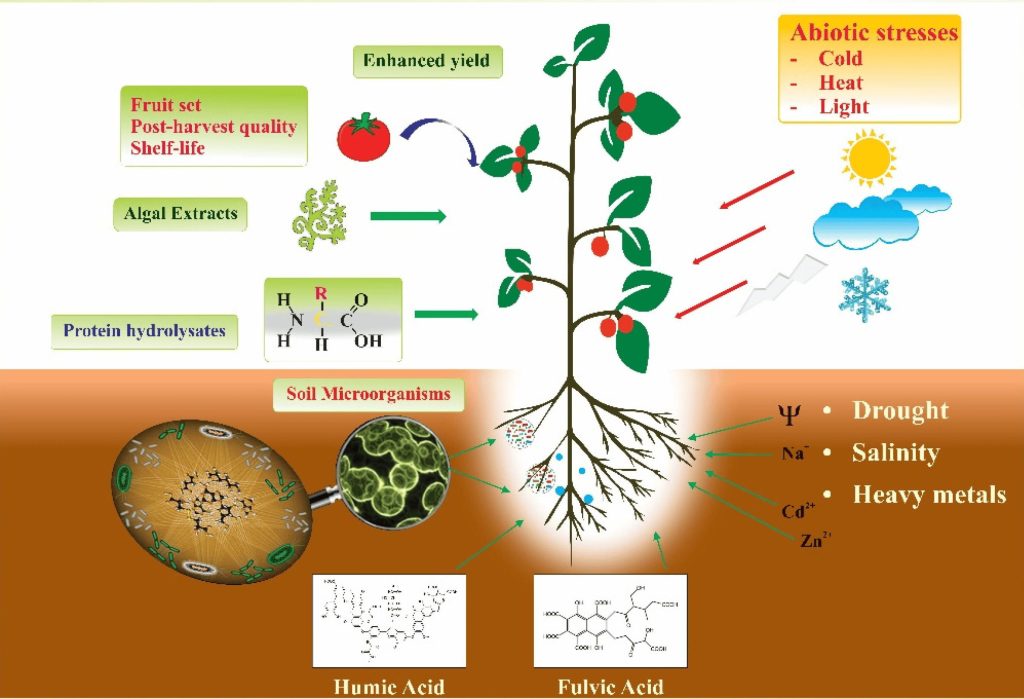
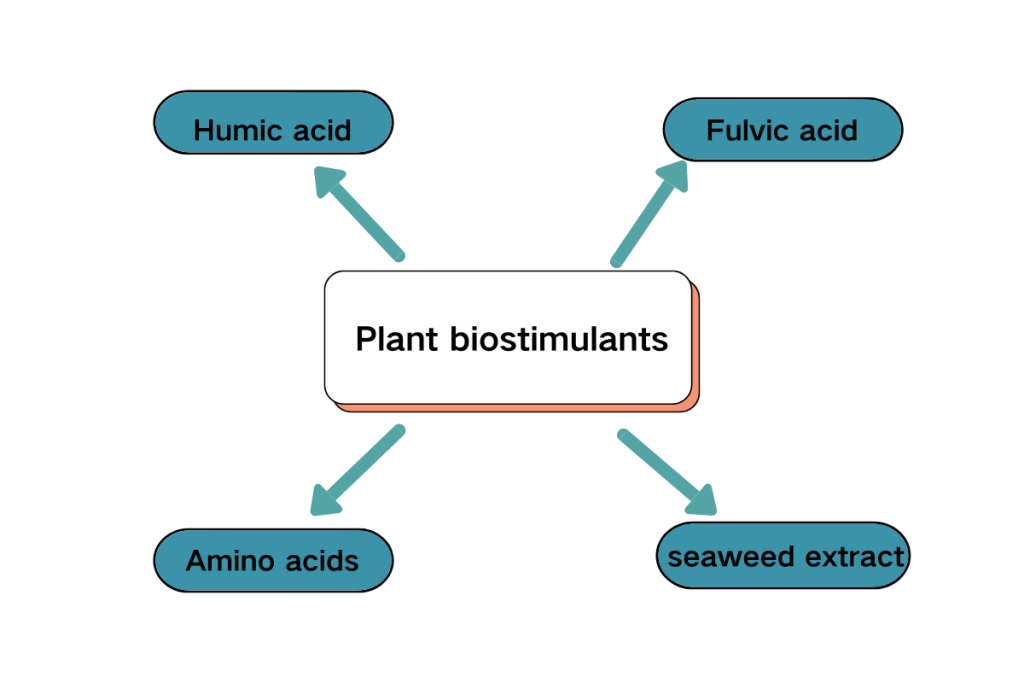
Types of Biostimulants
- Humus: Includes humic acid and fulvic acid, is derived from decomposed organic matter such as peat, lignite, or weathered lignite, and is a treasure trove of nutrients and bioactive compounds. Can enhance soil structure, and promote nutrient utilization, and microbial activity.
- Amino acids: It is an important component of protein and helps improve plant metabolism and stress resistance. Provides plants with a readily available source of nitrogen, which is essential for a variety of physiological processes including photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and enzyme activation.
- Seaweed Extract: Seaweed extracts derived from seaweed are rich in growth hormones (growth-promoting compounds such as cytokinins, auxins, and betaine) and micronutrients. Promotes plant growth and yield, making it a popular choice in biostimulant formulations.
Effects of Biostimulants in Agriculture on Plants
Biostimulants enhance soil health and microbial activity, creating a balanced ecology that supports plant growth. Stimulates plant development by interacting with plant physiology at the cellular and molecular levels.
1. Enhance nutrient absorption
Humic acid promotes healthy growth and development by increasing the efficiency of nutrient uptake by plant roots and cells, and biostimulants ensure plants receive essential elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients.
2. Root development
Healthy roots are essential for plant growth and productivity because they anchor the plant to the soil, absorb water and nutrients, and provide structural support. The alginic acid in the biostimulant promotes robust root development by stimulating root growth, increasing root branching, enhancing root hair formation, and improving root structure, laying a solid foundation for plant growth.

3. Improve plant growth and development
Biostimulants are plant growth regulators such as cytokinins, auxins, gibberellins, and abscisic acid that regulate various aspects of plant growth and development. Can affect cell division, elongation, differentiation, flowering, and fruit development, thereby improving crop yield and quality.
4. Enhance immunity
Plant diseases can destroy crops and cause severe yield losses. Biostimulants enhance plant immunity by activating defense mechanisms, inducing systemic resistance, and enhancing the plant’s ability to defend against pathogens. Making them more resistant to environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures helps reduce the incidence and severity of disease, ensuring healthier and more resilient plants.
5. Reduce chemical input
Fertilizers act as nutritional supplements for plants, providing essential elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, pesticides fight harmful pests and diseases, and biostimulants work on a more comprehensive level. They can boost plant metabolism, improve nutrient uptake, increase stress resistance, and promote overall plant health without directly providing nutrients or acting as pest control agents. This reduces reliance on fertilizers and chemicals, minimizing chemical inputs and environmental impact.
6. beneficial microorganisms
Biostimulants can stimulate beneficial microorganisms or activities in the soil, including mycorrhizal fungi, rhizosphere bacteria, and actinomycetes, forming a symbiotic relationship with plants, enhancing nutrient absorption, improving soil structure, and inhibiting pathogens.
Application of biostimulants
Biostimulants can be applied by a variety of methods, including foliar sprays, seed treatments, and soil leaching. The timing and frequency of application depend on plant species, growth stage, and environmental conditions.


Conclusions
Biostimulants are a cutting-edge approach to improving plant health, productivity, and agricultural resilience. By harnessing the power of natural compounds to enhance plant physiological processes, they become a valuable tool for increasing crop productivity, and promoting plant growth and recovery, while minimizing environmental impact. by harnessing the power of nature
External Link:
- Metabolic profile and antioxidant responses during drought stress recovery in sugarcane treated with humic acids and endophytic diazotrophic bacteria.
- Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture.
FAQs
Are biostimulants safe for the environment and human health?
Biostimulants are generally considered safe for the environment and human health. Because biostimulants are derived from natural sources and consist primarily of biologically active substances, they pose minimal risks to the environment and human health compared to synthetic chemicals.
Can biostimulants be used in combination with other agricultural inputs?
Yes, biostimulants can be used in combination with other agricultural inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides and soil amendments to increase their effectiveness and optimize plant growth. By incorporating biostimulants into a holistic crop management approach, farmers can synergistically benefit from the complementary effects of different inputs, improving overall crop performance and sustainability.
How do biostimulants differ from genetically modified organisms (GMOs)?
Biostimulants and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are different agricultural technologies with different modes of action and applications. Biostimulants are natural substances that enhance plant growth and performance through physiological processes, while GMOs involve genetic modification to introduce specific traits into plants, such as pest resistance or herbicide tolerance. Biostimulants do not involve genetic manipulation and are considered a more sustainable and environmentally friendly method of agriculture than GMOs.
What is the recommended use of biostimulants?
Recommended application methods for biostimulants vary based on product type and target crop. Biostimulants can be applied via foliar sprays, soil drenches, seed treatments, or irrigation systems to ensure proper uptake and efficacy. When using biostimulants, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consider factors such as plant growth stage, environmental conditions, and desired results to maximize their benefits and minimize potential risks.
Are there any regulatory guidelines for the use of biostimulants in agriculture?
Regulatory guidance on the use of biostimulants in agriculture varies between countries and regions, as biostimulants are a relatively new class of agricultural products subject to ever-changing regulations. In some regions, biostimulants may be classified as fertilizers, plant growth regulators, or biopesticides, each of which may have specific regulatory requirements for registration, labeling, and use.
